In the first year of the TCA, imports from the EU fell by -32%... Exports experienced a moderate fall of -3% for the whole of 2021, relative to what exports would have been without the agreement.
With trade data for the full year 2021 just released, we update our earlier estimates
of the UK-EU Trade and Cooperation Agreement’s impact on bilateral
trade between the UK and the EU for the first year of the agreement.
Although the TCA, signed between the UK and EU in a last-minute deal
on Christmas Eve 2020, came into being amidst much fanfare, the picture
of bilateral trade between both economies continues to be rather gloomy.
Using the latest release of HMRC data we estimate the impact of the TCA
on UK exports to, and imports from, the EU excluding gold trade.
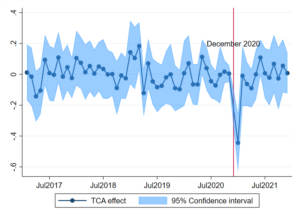
Data speak clearly. On the one hand, whilst UK exports
to the EU saw a jaw-dropping fall in January 2021 (-41%), exports
quickly recovered in subsequent months, resulting in a moderate fall of
-3% for the whole of 2021, relative to what exports would have been
without the agreement.
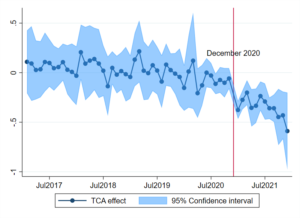
On the other hand, the effect of the TCA on UK imports
from the EU is strong and, more importantly, turns out to be much more
persistent. In the first year of the TCA, imports from the EU fell by
-32%. And what’s more, it almost looks as if EU imports would be on a
falling trajectory after the immediate hit in January 2021. The results
for estimated impacts on exports and imports are summarised in Figure 1.
Figure 1: the effect of the TCA on UK trade with the EU
Although the results on total trade show that the TCA did not affect
aggregate UK exports beyond January 2021, running the same
counterfactual analysis at a more disaggregated level reveals that EU
exports of certain broad product groups have been badly hit. In
particular, we find that the negative impact on UK exports of Leather
and Textile & Clothing (HS 41-43, 50-67) has been persistent across
all months of 2021. For these two sectors, the TCA reduced combined UK
exports to the EU by -59% or £5.7bn. The next most affected export
sector is Food and agriculture (HS 01-24). For this sector, the recovery
has been slower than for total exports, and over 2021 the TCA reduced
exports by 19% or £2.8bn.
For imports, differences across sectors are less pronounced. The most
affected sector is Chemicals and plastics, whose combined imports fell
by 39% (£19bn), followed by Machineries and transport equipment (-28% or
£29bn) and Metals (-28% or £4bn).
In summary, the TCA has had a strong and persistent effect on UK
imports from the EU, while the effect on total UK exports to the EU
appears to have been rather ephemeral in January 2021 only. That said,
looking beyond aggregate exports at product level data shows that UK
exports in particular sectors have also been severely hit.
One may ask what is driving these negative impacts. After all, in
the TCA, the provisions agreed on market access for goods ensure that,
at least in principle, trade between the two Parties remained
tariff-free and quota-free to minimise disruption for producers
exporting and importing goods to and from the EU. Practically, however,
we have seen that the disruption has been significant....
more at EU UK Trade Observatory
Key

Hover over the blue highlighted
text to view the acronym meaning

Hover
over these icons for more information

Comments:
No Comments for this Article